In the realm of Forex trading, numerous strategies exist to help traders maximize their returns. One such strategy is position trading, a method that's effective if well-understood and properly executed.
If you're looking for a more relaxed approach to investing, position trading might be the perfect strategy for you. Unlike day trading, which requires constant monitoring of the markets, position trading allows you to take a step back and focus on the bigger picture.
By holding investments for weeks, months, or even years, position traders aim to capitalize on long-term trends and significant price movements. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just starting, understanding the ins and outs of position trading can help you make more informed and profitable decisions.
👀 What is The Position Trading?

Position trading is a long-term Forex trading strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. Unlike short-term strategies like day trading or scalping, position trading relies heavily on fundamental analysis to predict long-term market trends.
In essence, a position trader is less concerned with minor market fluctuations and more focused on the overarching movements. They don't aim to exploit short-term market inconsistencies but are instead keen on capturing major price shifts resulting from macroeconomic changes.
Benefits of Position Trading
There are several benefits associated with position trading in Forex. Below, we've outlined a few key advantages:
While position trading offers numerous benefits, it's crucial to remember that it's not suitable for everyone. Traders need to have a deep understanding of fundamental analysis and the patience to wait for their trades to unfold. For those interested in exploring other trading strategies, consider looking into swing trading, trend trading, or breakout trading. Each strategy has its own unique approach and offers different advantages, so it's important to find the one that best fits your trading style and risk tolerance.
Developing a Position Trading Strategy
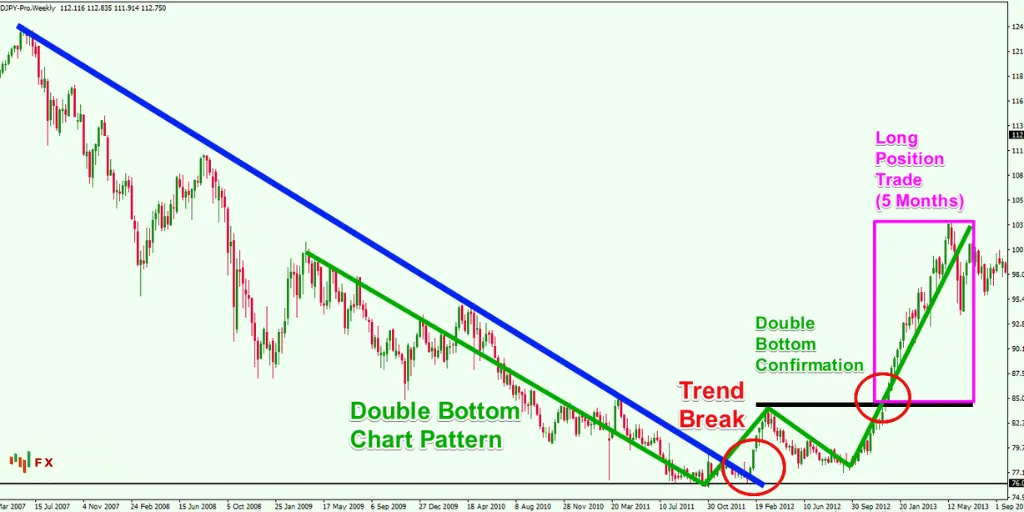
Creating a successful position trading strategy involves a combination of comprehensive market analysis, as well as meticulous risk management.
Market Analysis and Research
The foundation of any successful position trading approach lies in thorough market analysis and research. Traders need to have a deep understanding of both technical and fundamental aspects of the forex market.
Technical analysis involves studying price patterns, trends, and indicators to predict future price movements. By using charts and other technical tools, traders can identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
On the other hand, fundamental analysis focuses on economic indicators, geopolitical events, and other macroeconomic factors that can influence currency prices.
For a position trader, it's essential to regularly monitor economic calendars, news sources, and market reports. This can provide valuable insights into long-term market trends and potential trading opportunities.
Risk Management in Position Trading
Risk management is an integral part of a position trading strategy. Without a solid risk management plan, even the most well-researched trade can result in significant losses.
A key aspect of risk management in position trading includes determining the acceptable risk per trade, typically expressed as a percentage of the trader's total account balance. For instance, a trader might decide not to risk more than 1% of their account balance on a single trade.
| Account Balance | Risk per Trade (%) | Risk per Trade ($) |
|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 1% | $100 |
| $50,000 | 1% | $500 |
| $100,000 | 1% | $1000 |
Another important part of risk management is the use of stop-loss orders. A stop-loss order is designed to limit a trader's loss on a position in a security. By setting a stop-loss order, a trader determines in advance the level of loss they are willing to accept, thereby protecting their capital from significant market fluctuations.
It's also important to consider the risk-to-reward ratio of each trade. Ideally, the potential reward should outweigh the risk. For example, if a trader risks $100 on a trade, the potential profit should be more than $100 to justify the risk.
Identifying Entry and Exit Points
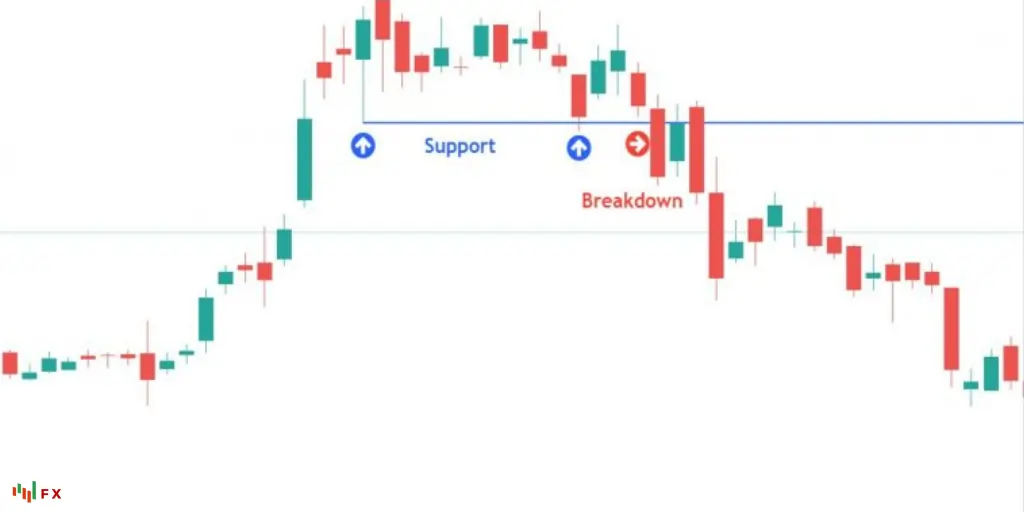
In position trading, one of the most critical steps is identifying appropriate entry and exit points. This involves using both technical and fundamental analysis to make informed decisions.
Technical Analysis for Entry and Exit
Technical analysis is a key tool in position trading, helping traders identify potential entry and exit points based on price patterns and market trends. Traders can utilize various technical indicators such as moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands to predict future price movements.
For example, a trader might enter a long position when a currency pair breaks above a resistance level or when a bullish trend is identified. Conversely, they might exit a position when a bearish reversal pattern is spotted or when the currency pair breaks below a support level.
Here is a simple example of how technical indicators might guide entry and exit points:
| Technical Indicator | Entry Point | Exit Point |
|---|---|---|
| Moving Average | Buy when the price moves above the moving average | Sell when the price moves below the moving average |
| RSI | Buy when RSI moves above 30 (oversold) | Sell when RSI moves above 70 (overbought) |
| Bollinger Bands | Buy when the price touches the lower band | Sell when the price touches the upper band |
Remember, while technical analysis can provide valuable insights, it's not infallible and should be used in conjunction with other tools and analysis methods.
Fundamental Analysis Considerations
In addition to technical analysis, fundamental analysis is also crucial in position trading. This involves examining economic indicators, political events, and other macroeconomic factors that can influence currency values.
For instance, a trader may enter a position based on positive economic data such as strong GDP growth or low employment rates in a particular country, indicating potential currency strength. Likewise, they might exit a position if there are signs of economic instability or political unrest that could negatively impact the currency value.
It's also important to keep an eye on central bank policies, as changes in interest rates can significantly affect currency values. For instance, a rate hike typically strengthens the currency, while a rate cut can weaken it.
Position Sizing and Leverage
In position trading, understanding two key aspects, position sizing and leverage is critical to effective risk management and maximizing potential returns.
Calculating Position Size
The position size in a trade refers to the number of units of security that a trader holds. Calculating the appropriate position size is a crucial aspect of risk management. It helps to limit potential losses to a fraction of the trader's total capital. Some traders use a fixed percentage of their trading capital to determine the position size, while others may adjust the size based on the volatility of the currency pair they are trading.
To calculate the position size, a trader needs to determine the risk per trade, the stop-loss level, and the pip value. The formula for position size is:
Position Size = (Account size * Risk per Trade) / (Stop Loss in Pips * Pip Value)
Here is an example of position size calculation:
| Account Size | Risk per Trade | Stop Loss in Pips | Pip Value | Position Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 1% | 50 | $0.1 | 2 standard lots |
Understanding Leverage in Position Trading
Leverage in position trading allows a trader to control a large position with a relatively small amount of capital. It's expressed as a ratio, such as 50:1, which signifies that a trader can control a $50 position for every $1 in their trading account.
While leverage can magnify profits, it can also amplify losses. Therefore, it's essential to understand and manage leverage effectively to prevent substantial losses. High leverage can lead to significant losses, especially in volatile forex markets. That's why experienced traders often advise using lower leverage or using no leverage at all, particularly when a trader is new to forex trading.
The formula for calculating leverage is:
Leverage = Total Value of Position / Trader's Investment
Here is an example of leverage calculation:
| Total Value of Position | Trader's Investment | Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| $100,000 | $1,000 | 100:1 |
Monitoring and Adjusting Positions
In the realm of position trading, a crucial and often overlooked aspect is the regular monitoring and potential adjustment of positions. This process can greatly impact the overall profitability and risk management of the trader's strategy.
Regular Monitoring of Positions
Regular scrutiny of open positions is a vital part of position trading. This involves keeping an eye on the market trends and how they're affecting the individual's trades. Traders need to stay updated with economic news and events that might influence the currency pairs they're trading.
In addition, traders need to regularly review their trading plan and ensure that their open positions still align with this strategy. For instance, if a position is opened based on a specific trend, and that trend changes, the trader might need to reconsider the position.
When to Adjust or Close Positions
Knowing when to adjust or close a position is an integral part of position trading. There are several factors a trader should consider when making this decision.
Knowing when to adjust or close positions in position trading is not an exact science and often involves a combination of technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and risk management. It's just as much an art as it is a science, requiring experience, judgment, and sometimes, a bit of luck.
Remember, the ultimate goal in position trading, just like in any other trading style such as swing trading or trend trading, is to maximize profits while minimizing losses. Regularly monitoring and wisely adjusting positions plays a crucial role in achieving this goal.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Position Trading

Mastery of position trading involves not just understanding the strategies but also being aware of common pitfalls. Even seasoned traders can make these mistakes, which can significantly impact the profitability of their trades.
Overleveraging
One of the most common mistakes in position trading is overleveraging. Leverage is a powerful tool in forex trading as it allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. However, if not used wisely, it can lead to substantial losses.
Overleveraging occurs when a trader takes on a position size that is too large compared to their account size. This can magnify both potential gains and losses. However, if the market moves against the position, the losses can be significant and may even exceed the trader's initial investment.
Traders should carefully consider their leverage and ensure it aligns with their risk tolerance and trading strategy. It's also important to have a solid understanding of how leverage works in position trading.
Ignoring Risk Management Principles
Position trading, like all trading styles, involves risk. Ignoring risk management principles is another common mistake that can lead to substantial losses.
Some traders focus solely on potential profits without considering the risks involved. This can lead to poor decision-making, such as holding onto losing positions for too long in the hope that the market will turn around.
Proper risk management involves setting stop-loss and take-profit levels, diversifying trading positions, and never risking more than a small percentage of the trading account on any single trade. Traders should also regularly review their trading performance and adjust their strategies as needed.
Emotional Trading Biases
Forex trading requires a high level of discipline and emotional control. Emotional trading biases, such as fear, greed, or overconfidence, can lead to irrational decisions that deviate from the trading plan.
For instance, fear can cause traders to exit winning positions too early, while greed can lead them to hold onto losing positions in the hope of a market reversal. Overconfidence, on the other hand, can lead to overtrading or taking on larger positions than justified by the market conditions.
Traders should strive to maintain a calm and objective mindset when trading. They should base their trading decisions on careful analysis and a well-defined trading plan, not on emotions.
Common Queries Related to Position Trading
What is Position Trading?
How does Position Trading differ from Day Trading?
What are the primary benefits of Position Trading?
What are the main risks associated with Position Trading?
What Strategies do Position Traders commonly use?
What types of analysis do Position Traders use?
How do Position Traders manage risk?
What kind of market conditions are ideal for Position Trading?
💭 Conclusion
Position trading stands out as a compelling strategy for those with a long-term investment horizon and a keen eye for market trends. By focusing on broader movements rather than daily fluctuations, position traders can capitalize on significant price shifts over extended periods.
This approach not only demands patience and discipline but also a thorough understanding of both technical and fundamental analyses. While the potential for substantial returns is high, so are the risks, making it crucial for traders to stay informed and vigilant. Ultimately, position trading offers a balanced blend of strategy and insight, making it a valuable option for discerning investors.

![Earnings Per Share (EPS) in Forex Trading 📖 Forex Glossary [2025 Edition] 5 Earnings per Share (EPS)](https://fxparkey.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Earnings-per-Share-EPS-300x189.webp)