Smart Money Concepts have developed as a potent trading strategy that concentrates on comprehending and utilizing the actions of institutional investors, frequently called “smart money.” By examining the market movements driven by these powerful players, traders can acquire valuable insights and make more knowledgeable trading decisions.
In this article, we will inquire about the basics of Smart Money Concepts, essential terminology, and strategies to help you manage through the intricate world of trading.
🤔 What are Smart Money Concepts?
Smart Money Concepts revolve around the idea that institutional investors, such as banks, hedge funds, and large financial institutions, have a significant impact on market trends due to their substantial capital and market expertise. These entities are considered “smart money” because they possess the resources and knowledge to make well-informed investment decisions.
Smart Money Trading strategies aim to identify and follow the footprints of smart money, allowing retail traders to align their trades with the actions of these major market participants. By understanding the supply and demand dynamics created by institutional investors, traders can potentially increase their chances of success in the market.
Key Terminology in Smart Money Concepts
To effectively implement Smart Money Concepts, it's essential to understand the following key terms:
1. Order Blocks
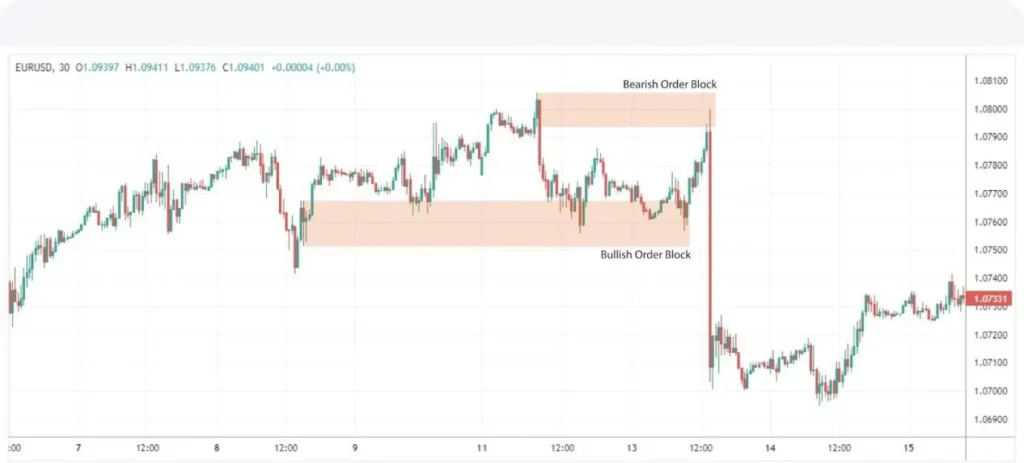
These are significant price levels where large institutional investors place substantial orders, often resulting in a notable change in price direction. Order blocks are crucial in Smart Money Concepts analysis as they represent areas of high interest for smart money. Traders look for these zones to anticipate potential reversals or continuations of trends. Identifying order blocks can provide valuable insights into where major players are entering or exiting the market, allowing retail traders to align their strategies with institutional movements.
2. Fair Value Gaps
These are price discrepancies that occur when an asset is trading above or below its perceived fair market value, often due to market manipulation by smart money. Fair value gaps represent imbalances in supply and demand, typically created by sudden, large-volume trades. These gaps are expected to be “filled” as the market seeks equilibrium. Traders using Smart Money concept strategies pay close attention to these gaps as potential entry or exit points, anticipating that prices will eventually return to their fair value.
3. Liquidity
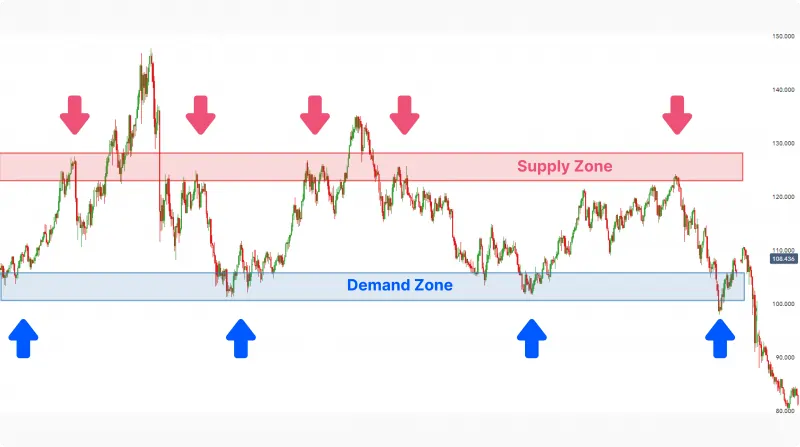
In Smart Money Concepts, liquidity refers to the volume of trading activity in the market and plays a crucial role in understanding smart money movements. Smart money often leverages liquidity to its advantage, executing large trades that can significantly influence price movements. High liquidity areas are where institutional investors can enter or exit positions without causing drastic price changes. Retail traders can use liquidity analysis to identify potential areas of smart money activity and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
4. Breaker Blocks
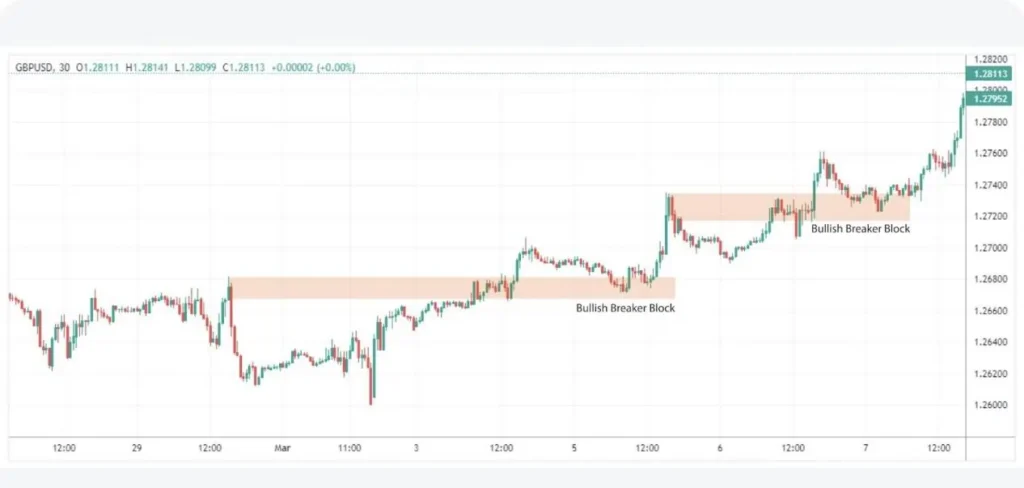
These are critical price levels that, when broken, indicate a potential shift in market sentiment and a possible trend reversal. Breaker blocks are formed when a strong move in one direction is followed by a consolidation and then a break in the opposite direction. They represent areas where smart money may be accumulating or distributing positions. Traders look for breaker blocks to identify potential trend changes and new trading opportunities.
5. Mitigation Blocks
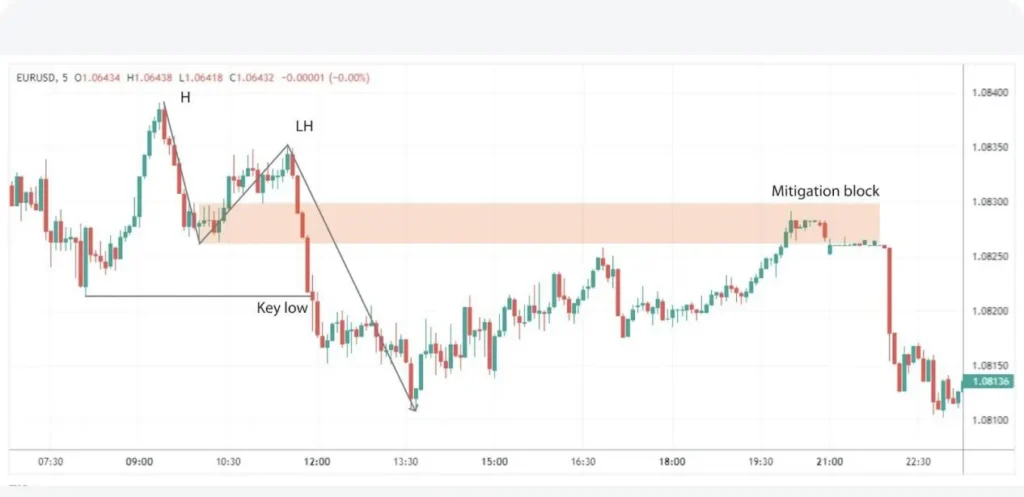
These are strategic price levels where smart money may place orders to mitigate potential losses or protect their positions. Mitigation blocks often coincide with significant support or resistance levels and can be used to identify areas where smart money is likely to intervene in the market. Traders using Smart Money concept strategies look for these blocks to anticipate potential price reactions and plan their entries and exits accordingly. Understanding mitigation blocks can help traders align their risk management strategies with those of institutional investors.
Strategies for Implementing Smart Money Concepts

To successfully implement Smart Money Concepts in your trading, consider the following strategies:
- Identify SMC Zones: Analyze price charts to identify key SMC zones, such as order blocks, fair value gaps, and liquidity levels. These zones can provide valuable entry and exit points for your trades.
- Confirm with Multiple Timeframes: Validate the significance of SMC zones by analyzing them across multiple timeframes. Confluence between timeframes can increase the reliability of your analysis.
- Use Volume Analysis: Pay attention to trading volume, as it can indicate the presence of smart money. Unusual volume spikes or drops can signal institutional activity.
- Combine with Other Tools: Integrate SMC analysis with other technical analysis tools, such as support and resistance levels, trend lines, and indicators, to form a comprehensive trading strategy.
- Manage Risk: Always practice proper risk management techniques, such as setting stop-losses and managing position sizes, to protect your capital.
Comparing Smart Money Concepts with Traditional Trading Strategies
| Aspect | Smart Money Concept | Traditional Trading Strategies |
|---|---|---|
Focus | Institutional activity | Price action, indicators |
Terminology | Order blocks, fair value gaps, liquidity | Support, resistance, trends |
Timeframes | Multiple timeframes for confirmation | Varies based on strategy |
Risk Management | Emphasized as a crucial component | Varies based on individual approach |
While Smart Money Concepts introduce new terminology and focus on institutional activity, they share similarities with traditional trading strategies in terms of risk management and the use of multiple timeframes for analysis.
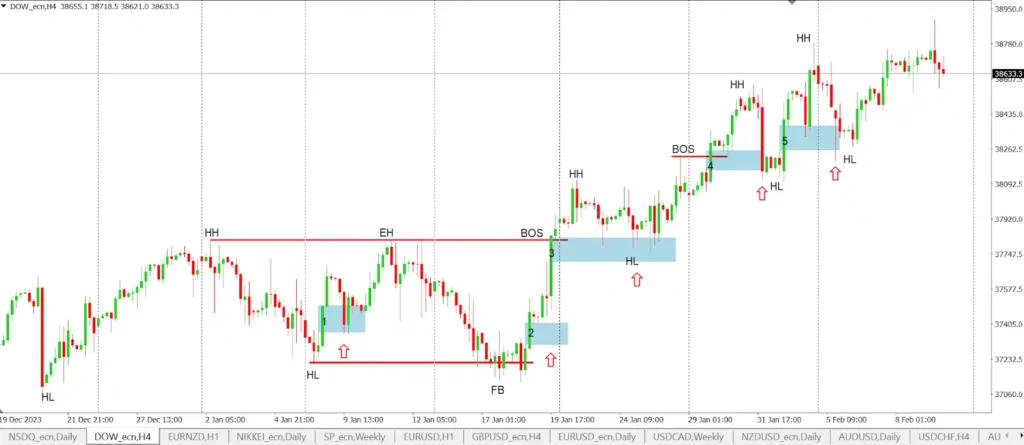
🔎 Identifying Smart Money

Unusual Trading Volume
One of the primary signals of smart money activity is the unusually high trading volume in a stock or asset without any corresponding public news or information to justify it.
This can indicate that institutional investors or other knowledgeable players are making significant moves.
Insider Buying
Insider buying, where company executives or board members purchase shares of their own company, can signal confidence in future prospects. Insiders have additional information about their company, so their purchases may indicate positive undisclosed developments. Legitimate insider buying is legal and publicly disclosed.
Focus on High-Growth Sectors
Smart money tends to focus on sectors and industries with strong growth potential, such as technology, renewable energy, and healthcare. Monitoring smart money movements in promising sectors can help identify emerging trends. Growth stocks are also a common target.
Options Activity
Analyzing stock pricing and index options can provide clues about how smart money is positioned for future trades. Unusual options activity, such as large purchases of call options, can hint at bullish sentiment among informed investors.
Regulatory Filings
Tracking regulatory filings like 13F reports, which disclose the holdings of large institutional investors, can provide insights into smart money movements. The Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) also requires large traders to report positions, which are published in Commitments of Traders (COT) reports.
Volatility and Momentum
High levels of market volatility coupled with large trading volumes may indicate the presence of smart money. Retail investors typically can't create enough volatility to move market trends, so spikes in volatility along with volume can signal institutional activity. Aggressive buying or selling leading to significant price movements after a period of stability is another potential sign.
The Role of Technology in Smart Money Concepts
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced the implementation of Smart Money Concepts. Powerful charting tools, algorithmic trading, and real-time data analysis have made it easier for retail traders to identify and respond to institutional activity.
Traders can now automate the identification of Smart Money Concept patterns and execute trades based on predefined criteria, improving efficiency and accuracy. However, it's crucial to thoroughly backtest and optimize algorithms before deploying them in live trading.
Tracking Smart Money
Monitor unusual trading volume
Analyze insider buying
Focus on sectors and stocks with high growth potential
Utilize options and pricing data
Track regulatory filings
Use on-chain analytics for crypto
Combine multiple indicators
Be aware of limitations
Smart Money Information Center
What are Order Blocks in SMC?
Order blocks are price levels where large institutional orders are placed, often leading to significant price direction changes.
How does SMC differ from Traditional Price Action Trading?
Smart Money Concept uses unique terminology and focuses more on institutional behavior, while still incorporating many principles of price action trading.
What are Fair Value Gaps in Smart Money Concepts?
Fair value gaps are price discrepancies where an asset trades above or below its perceived fair market value.
How can Retail Traders identify Smart Money movements?
Traders can analyze unusual trading volume, insider buying, regulatory filings, and specific chart patterns to identify Smart Money movements.
What is a liquidity grab in Smart Money Trading?
A liquidity grab is when the price briefly moves beyond a key level to trigger stop losses before reversing.
Are Smart Money Concepts applicable to all Financial Markets?
Yes, Smart money concept principles can be applied to various markets, including forex, stocks, cryptocurrencies, and futures.
What are the main criticisms of Smart Money Concepts?
Critics argue that the Smart Money Concept lacks empirical evidence, overcomplicates price action, and may not accurately represent institutional trading behavior.
🔗 Conclusion

Smart Money Concepts offer traders a powerful framework for understanding and capitalizing on the actions of institutional investors in the financial markets. By identifying Smart Money Concepts' key zones, such as order blocks, fair value gaps, and liquidity levels, traders can potentially align their strategies with those of major market participants. However, it's crucial to approach Smart Money Concepts trading with caution and a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics.
Successful implementation of Smart Money Concepts requires continuous learning, adaptation, and the integration of multiple analytical tools. While Smart Money Concepts can provide valuable insights, they should be used in conjunction with sound risk management practices and a well-rounded trading strategy. As with any trading approach, there are no guarantees and market conditions can change rapidly. Ultimately, Smart Money Concepts serve as a valuable addition to a trader's toolkit, potentially enhancing decision-making and market analysis.






