
The Smart Money Concept (SMC) is an advanced trading approach that aims to identify and capitalize on the actions of institutional investors in the forex market. One of the key components of this strategy is the mitigation block, a powerful tool for understanding market dynamics and predicting potential reversals.
🔗 Understanding Mitigation Blocks
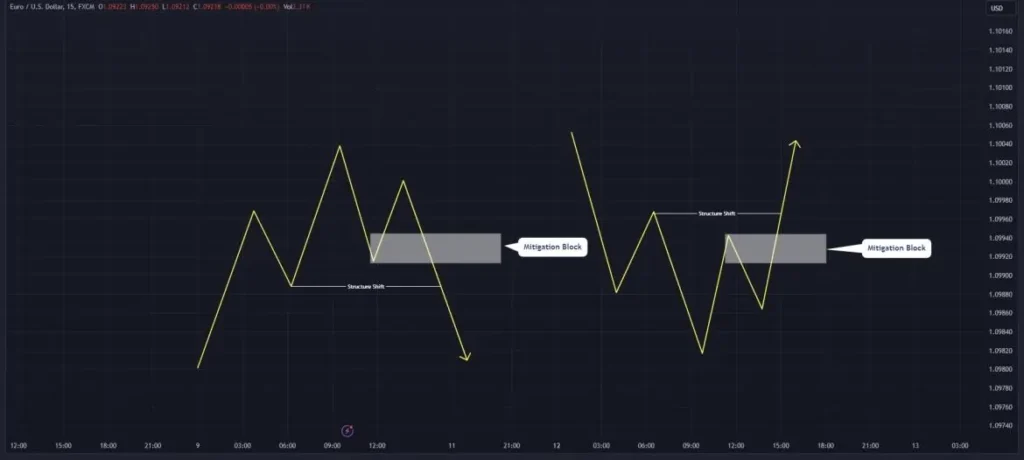
A mitigation block is a specific price area on a chart that indicates where previous price movements have stalled and reversed.
These blocks are formed when the market fails to create a new higher high in an uptrend or a new lower low in a downtrend, signaling a potential shift in market direction.
📌 Importance of Mitigation Blocks
Mitigation blocks are powerful tools for pinpointing areas where the market has previously demonstrated weakness or strength, indicating a possible change in direction. These zones are critical because they often represent areas of significant institutional activity.
By recognizing these zones, traders can anticipate potential trend reversals before they occur, allowing for more proactive trading decisions. Mitigation frequently aligns with other technical indicators, providing stronger confirmation of potential reversals when used in conjunction with support/resistance levels, trend lines, or other SMC concepts like order blocks. This confluence of factors increases the reliability of the signals generated by mitigation blocks.
Mitigation blocks serve as excellent reference points for optimizing trade entries and exits. They allow traders to fine-tune their entry points, potentially improving the risk-reward ratio of their trades by entering closer to key reversal points.
For exit strategies, traders can use mitigation blocks to plan more effectively, whether taking profits or cutting losses. Advanced traders can implement scaling strategies, entering or exiting positions in stages as price interacts with these key levels. This strategic approach to entries and exits can significantly enhance overall trading performance and profitability.
The use of mitigation blocks significantly contributes to robust risk management strategies. Traders can place stop losses just beyond the mitigation block, providing a logical and data-driven approach to risk control.
By entering trades near mitigation blocks and placing stops beyond them, traders can often achieve more favorable risk-reward ratios. Additionally, mitigation blocks help traders account for market volatility, as these areas often represent zones where price action has previously stabilized or reversed. This consideration of volatility can lead to more precise risk assessment and position sizing, ultimately protecting trading capital more effectively.
Types of Mitigation Blocks
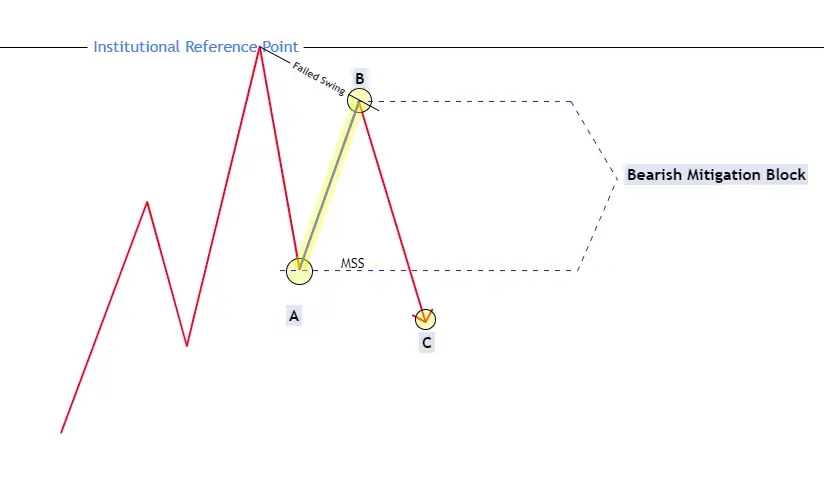
- Bearish Mitigation Block
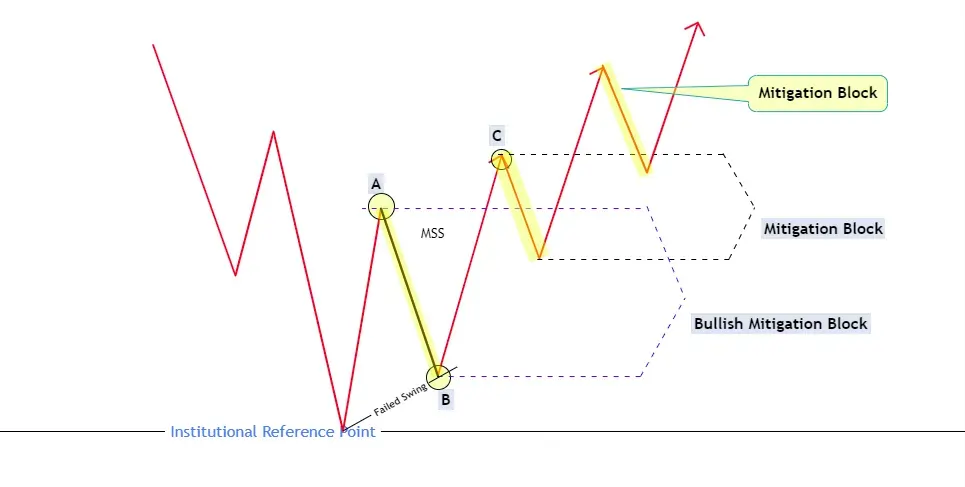
- Bullish Mitigation Block
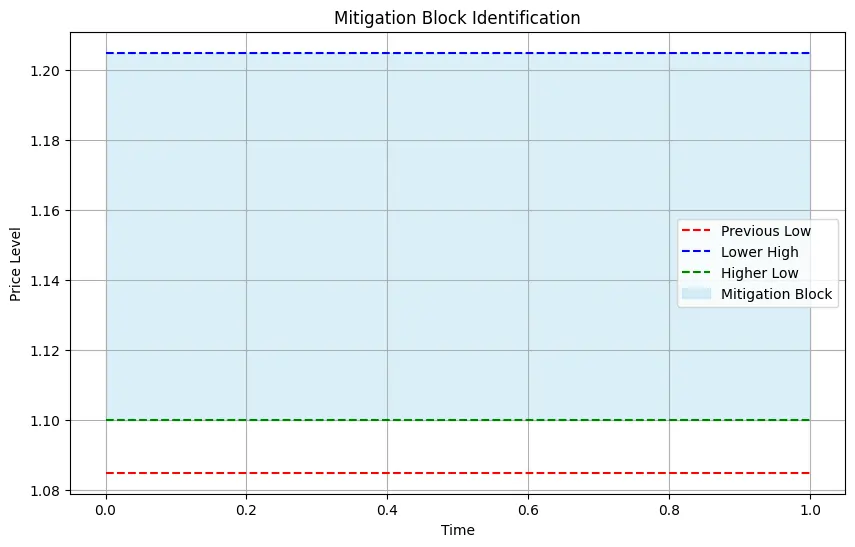
Identifying Mitigation Blocks
- Locate a Higher Timeframe Point of Interest (POI):
To begin identifying a mitigation block, traders should first focus on locating a Point of Interest (POI) on a higher timeframe chart. This POI could be an order block, which represents a significant level where large orders were placed, a Fair Value Gap (FVG), indicating a price level where the market has moved away from its perceived fair value, or a rejection block, signaling a level where the price has previously reversed. By identifying these key levels on a higher timeframe, traders can anticipate potential reversals and use them as a foundation for locating mitigation blocks on lower timeframes.
- Observe Price Action on Lower Timeframes:
After identifying a higher timeframe POI, traders should shift their attention to lower timeframe charts to observe the price action around that level. The key is to look for a failure in the price to break the current trend's structure, followed by a significant shift in the market structure. For example, in an uptrend, if the price fails to create a new higher high and instead forms a lower high before breaking below the previous low, it indicates a potential bearish mitigation block. Conversely, in a downtrend, if the price fails to create a new lower low and instead forms a higher low before breaking above the previous high, it suggests a potential bullish mitigation block.
- Mark the Mitigation Block:
Once a failure in the trend structure and a subsequent market structure shift have been identified on the lower timeframe, traders should mark the mitigation block. To do this, locate the last significant candle before the failed rally or decline. This candle often represents the last point of buying or selling pressure before the price reverses. Mark the area from the high to the low of this candle, as this range defines the mitigation block. It is essential to be precise when marking the block, as this level will serve as a key reference point for potential future reversals and trading opportunities.
Trading Strategies Using Mitigation Blocks

Incorporating mitigation blocks into your trading strategy can significantly improve your decision-making process.
Here are some effective approaches:
1. Counter-Trend Trading
When a mitigation block forms, it often signals a potential reversal. Traders can enter counter-trend positions when the price revisits the mitigation block, anticipating a reversal.
2. Trend Continuation
In some cases, mitigation blocks can act as areas of temporary pause in a strong trend. Traders can use these blocks to enter positions in the direction of the overall trend at more favorable prices.
3. Combining with Other Technical Tools
For increased accuracy, combine mitigation blocks with other technical analysis tools such as support and resistance levels, trend indicators, and candlestick patterns.
Common Questions
How are Mitigation Blocks Formed?
Mitigation blocks form when the market fails to create new highs or lows, signaling a potential shift.
How do Bearish Mitigation Blocks form?
Bearish mitigation blocks form during uptrends when the price fails to make a new higher high.
What do Bullish Mitigation Blocks indicate?
Bullish mitigation blocks indicate a potential shift from bearish to bullish market sentiment.
Why are Mitigation Blocks important in SMC Trading?
Mitigation blocks help identify potential reversal zones, improve entry/exit points, and enhance risk management.
How can Traders identify Mitigation Blocks?
Traders can identify mitigation blocks by locating POIs, observing price action, and marking the blocks.
What Trading Strategies can be used with Mitigation Blocks?
Counter-trend trading, trend continuation, and combining with other technical tools are effective strategies.
Should Traders rely solely on Mitigation Blocks?
No, traders should use a comprehensive approach combining various tools and strategies.
What is the key to Mastering Mitigation Blocks in SMC Trading?
Continuous learning, practice, and adaptation are key to mastering mitigation blocks in SMC trading.
🔗 Conclusion

Mitigation blocks are a valuable component of the Smart Money Concept, offering traders insights into potential market reversals and optimal entry and exit points. By understanding how to identify and utilize these blocks effectively, traders can enhance their decision-making process and potentially improve their trading results.
However, it's important to remember that no single indicator or concept should be relied upon exclusively. Successful trading requires a comprehensive approach that combines various tools and strategies while maintaining strict risk management practices. As with any trading technique, continuous learning, practice, and adaptation are key to mastering the use of mitigation blocks within the Smart Money Concept framework.







