Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are a crucial component of the Smart Money Concept (SMC) in trading. These gaps represent areas of imbalance in the market, often created by significant institutional trading activity. Understanding and utilizing FVGs can provide traders with valuable insights into potential price movements and trading opportunities.
📌 What is a Fair Value Gap?

A Fair Value Gap is a price level or zone where there is a significant imbalance between buying and selling pressure, typically caused by rapid price movements. In the context of SMC, these gaps are believed to be created by large institutional traders, often referred to as “smart money.” FVGs occur when the price of an asset moves so quickly that it leaves behind an area where no trading has taken place.
Characteristics of Fair Value Gaps
Fair Value Gaps have several key characteristics:
🤔 Why are Fair Value Gaps important?
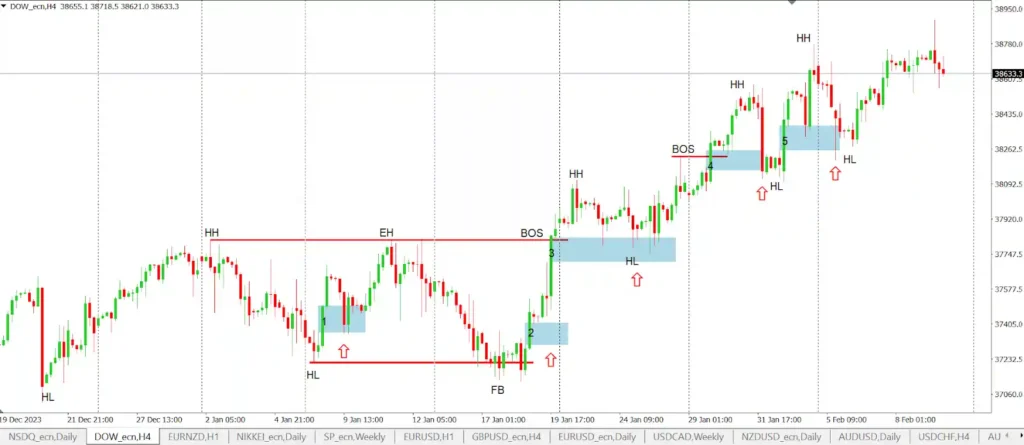
Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) are important in trading because they provide valuable insights into market dynamics and potential price movements. These gaps represent areas of significant imbalance between buying and selling pressures, often created by large institutional trades or sudden market events.
FVGs are crucial for several reasons: they highlight market inefficiencies that traders can potentially exploit, serve as potential support or resistance levels, and offer clues about institutional activity or “smart money” movements. Traders use FVGs to identify potential entry and exit points, set price targets, and confirm trend directions. Additionally, FVGs can help in understanding market sentiment and liquidity flows.
By recognizing and utilizing Fair Value Gaps, traders can gain a competitive edge in their analysis, improve their timing for trades, and potentially increase their profitability. However, it's important to note that FVGs should be used in conjunction with other technical and fundamental analysis tools for a comprehensive trading strategy, as they are just one piece of the larger market puzzle.
Identifying Fair Value Gaps
Types of Fair Value Gaps
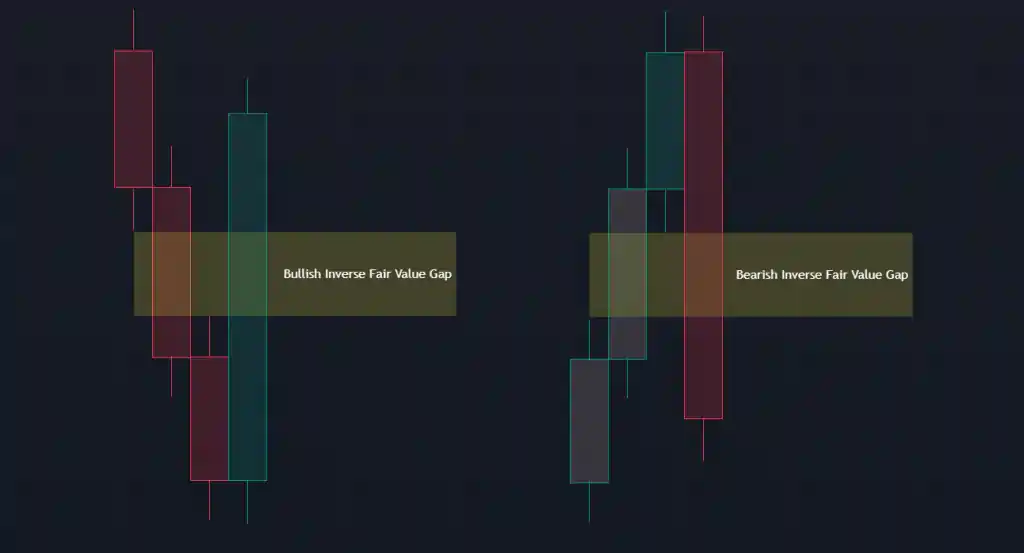
Fair Value Gaps come in two primary forms:
The Significance of Fair Value Gaps in SMC
In the Smart Money Concept, Fair Value Gaps are considered important for several reasons:
Market Inefficiency: FVGs represent areas where the market has moved too quickly, creating an inefficiency that the market often seeks to correct.
Potential Reversal Points: These gaps often act as support or resistance levels, potentially leading to price reversals.
Institutional Activity: Large FVGs are often associated with significant institutional trading activity, providing insights into the actions of “smart money.”
Price Targets: Traders often use FVGs as potential price targets, expecting the market to return to these levels to “fill the gap.”
Trading Strategies Using Fair Value Gaps
Traders can incorporate Fair Value Gaps into their strategies in several ways:
Considerations When Trading Fair Value Gaps
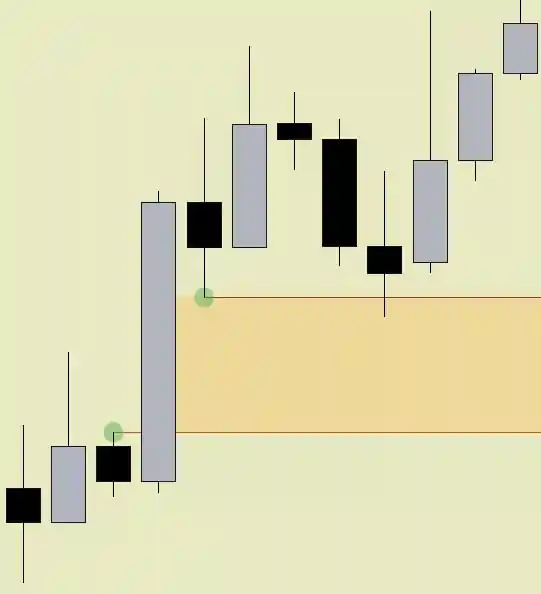
While Fair Value Gaps can be powerful tools in a trader's arsenal, it's important to consider the following:
Help Section
Why are Fair Value Gaps Important in Trading?
FVGs indicate market inefficiencies, potential reversal points, and institutional activity, providing valuable insights for trading decisions and strategy development.
How do Traders use Fair Value Gaps in their Strategies?
Traders use FVGs for entry points, stop loss placement, profit targets, and support/resistance levels in their trading strategies.
Do all Fair Value Gaps get filled?
Not all FVGs are filled. Some may remain unfilled or only partially filled, especially in strong trending markets.
What Timeframes are best for identifying Fair Value Gaps?
FVGs can be identified on multiple timeframes, but higher timeframe gaps are generally considered more significant for trading decisions.
How are Fair Value Gaps Related to Institutional Trading?
Large FVGs are often associated with significant institutional trading activity, providing insights into the actions of “smart money” in the market.
Can Fair Value Gaps be used for Breakout Confirmation?
Yes, traders often look for FVGs in the breakout direction to confirm the validity of a price breakout.
What are the limitations of Trading with Fair Value Gaps?
Limitations include subjectivity in identification, the potential for false signals, and the risk of overreliance without considering other market factors.
📌 Conclusion

Fair Value Gaps are a powerful concept within the Smart Money framework, offering traders a unique perspective on market dynamics and potential price movements. By understanding how to identify and interpret these gaps, traders can gain insights into institutional activity and potential market inefficiencies.
However, like all trading concepts, Fair Value Gaps should not be used in isolation. They are most effective when combined with other technical analysis tools, fundamental analysis, and a comprehensive understanding of market dynamics. Traders should always practice proper risk management and thoroughly backtest any strategy before implementing it in live trading.
As the financial markets continue to evolve, the concept of Fair Value Gaps remains a valuable tool for traders seeking to understand and capitalize on market inefficiencies. By mastering this aspect of the Smart Money Concept, traders can enhance their ability to identify high-probability trading opportunities and potentially improve their overall trading performance.







