
Forex trading strategies are crucial tools for success in the foreign exchange market. These strategies help traders identify profitable opportunities and manage risk effectively. In this article, we will explore various forex trading strategies, their benefits, and how to implement them effectively.
🔗 What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies in the global market. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Forex traders aim to profit from the fluctuations in exchange rates between currency pairs, such as the Euro and the US Dollar (EUR/USD) or the British Pound and the Japanese Yen (GBP/JPY). Successful forex trading requires a solid understanding of market dynamics, economic factors, and technical analysis. Traders employ various strategies, such as trend following, range trading, or breakout trading, to identify profitable opportunities and manage risk in this fast-paced and dynamic market.
Understanding Forex Trading Strategies
A forex trading Strategies is a systematic approach to buying and selling currencies in the foreign exchange market. These strategies typically incorporate elements such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis, risk management, entry and exit rules, and position sizing.
📌 Popular Forex Trading Strategies
Trend Following Strategy
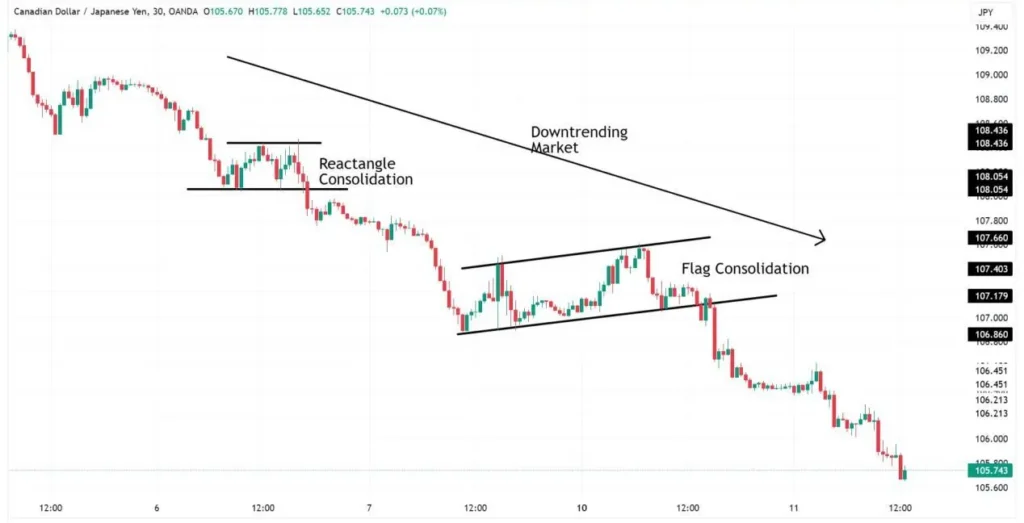
Trend following is a popular and time-tested Forex Trading Strategies that involves identifying the direction of market momentum and entering trades that align with the prevailing trend. This approach is based on the principle that prices tend to move in sustained directions over time, creating opportunities for traders to profit from these extended movements.
Key Principles
- Trend Identification: Traders use various technical analysis tools and indicators to determine the overall direction of the market. This may involve analyzing price action, chart patterns, and trend lines.
- Momentum Confirmation: Once a trend is identified, traders look for confirmation of momentum using indicators such as Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), Relative Strength Index (RSI), or Average Directional Index (ADX).
- Entry Timing: Traders enter positions in the direction of the trend, often waiting for pullbacks or consolidations to find optimal entry points.
- Risk Management: Implementing stop-loss orders and proper position sizing to protect against potential losses if the trend reverses.
- Exit Strategy: Traders typically hold positions until there are clear signs of trend reversal or until predetermined profit targets are reached.
Implementation:
Range trading Strategy
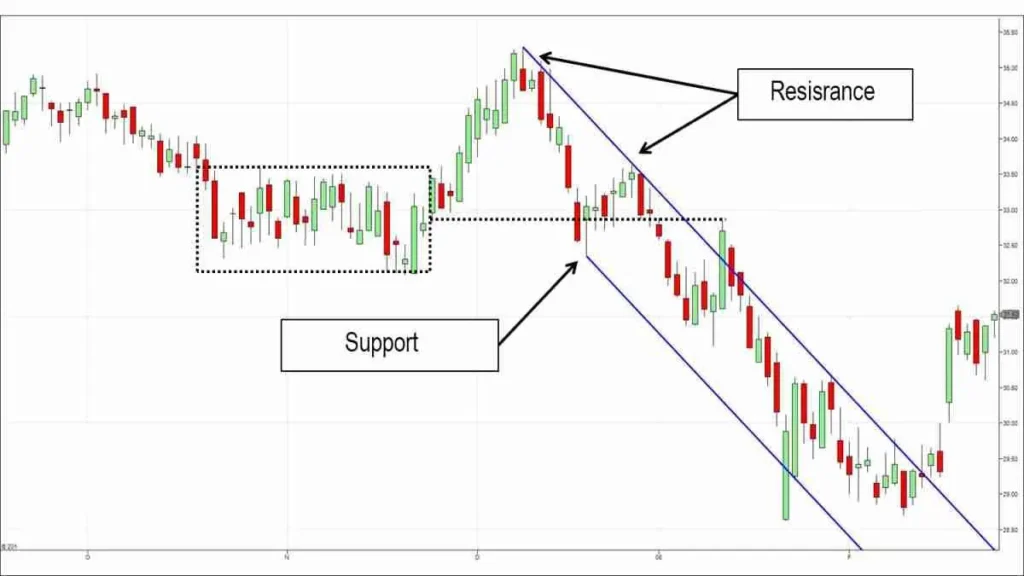
Range trading is a forex Trading Strategies that capitalizes on markets moving sideways within a defined price range. This strategy is based on the principle that prices often oscillate between two levels, known as support and resistance, without establishing a clear upward or downward trend. Range traders aim to profit from these price fluctuations by buying at support levels and selling at resistance levels.
Key Principles
- Identifying Range Boundaries: Traders use technical analysis tools, such as horizontal lines, Fibonacci retracements, or pivot points, to determine the upper and lower limits of the price range.
- Support and Resistance: Support is the lower boundary of the range, where buying pressure is expected to overcome selling pressure, causing prices to bounce back up. Resistance is the upper boundary, where selling pressure is expected to exceed buying pressure, causing prices to retreat.
- Oscillators: Traders often employ oscillators, such as the Relative Strength Index (RSI) or Stochastic, to gauge whether the market is overbought or oversold within the range.
- Entry and Exit Points: Range traders typically enter long positions near the support level and short positions near the resistance level. They exit positions when prices reach the opposite boundary or when there are signs of a breakout.
- Risk Management: Stop-loss orders are placed outside the range to protect against potential losses if the range is broken. Take-profit orders are set near the opposite boundary to lock in profits.
Implementation:
Breakout Trading Strategy
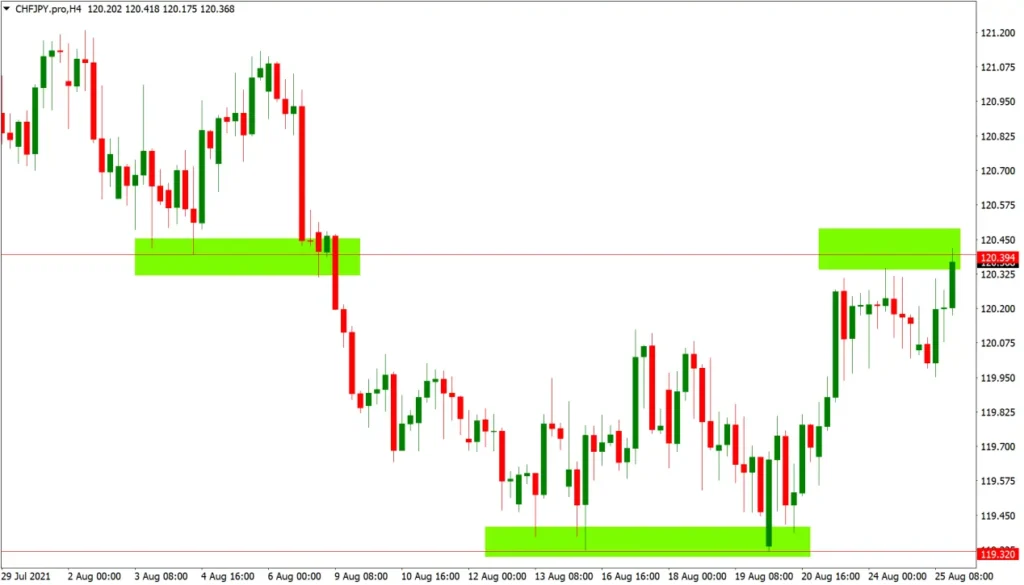
Breakout trading is a dynamic Forex Trading Strategies that involves entering the market when the price moves beyond a defined support or resistance level, anticipating that the move will continue in the breakout direction. This strategy capitalizes on the potential for significant price movements that often occur when key levels are breached, signaling a shift in market sentiment or the beginning of a new trend.
Key Principles
- Identifying Key Levels: Traders use technical analysis to pinpoint crucial support and resistance levels. These may include horizontal price levels, trendlines, chart patterns, or psychological round numbers.
- Volume Confirmation: A surge in trading volume often accompanies genuine breakouts, providing additional confirmation of the move's strength and potential sustainability.
- Entry Timing: Traders typically enter positions as soon as the price convincingly breaks through the identified level. Some may wait for a retest of the broken level for additional confirmation.
- Stop Loss Placement: Stop-loss orders are usually placed just below the breakout level for long positions or above for short positions to protect against false breakouts.
- Take Profit Targets: Profit targets can be set using various methods, such as measuring the height of the previous range or using Fibonacci extensions.
Breakout Types
- Range Breakouts: When price breaks out of an established trading range.
- Pattern Breakouts: Breaks from chart patterns like triangles, flags, or head and shoulders.
- Trendline Breakouts: When price breaks above or below significant trendlines.
Implementation:
Carry Trade Strategy
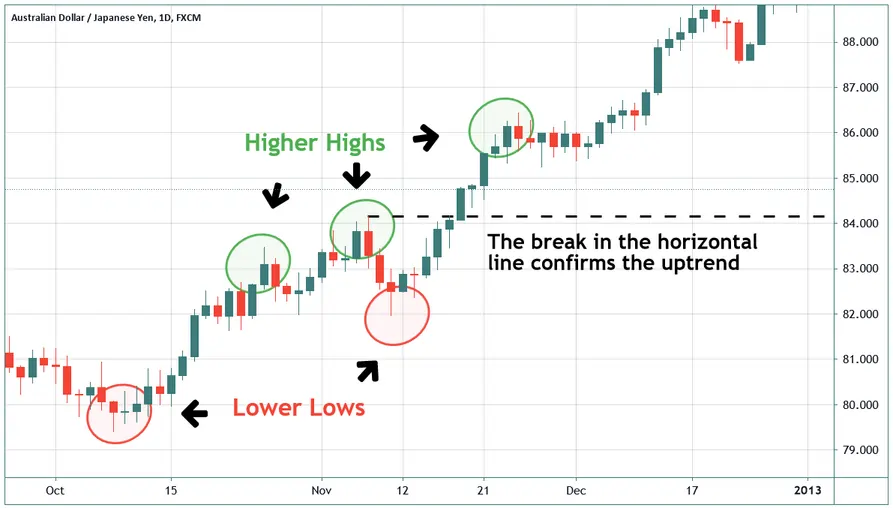
The carry trade strategy is a popular approach in Forex Trading Strategies that involves borrowing a currency with a low interest rate and simultaneously investing in a currency with a higher interest rate. The goal is to profit from the interest rate differential between the two currencies, known as the “carry.” This strategy aims to capitalize on the fact that currencies with higher interest rates tend to appreciate against those with lower interest rates over time.
Key Principles
- Interest Rate Differentials: Carry traders seek currency pairs with significant interest rate differences. The larger the differential, the more attractive the carry trade opportunity.
- Long-Term Holding: Carry trades are typically held for extended periods, ranging from weeks to months or even years, to allow the interest rate differential to accumulate.
- Positive Carry: A positive carry occurs when the interest earned on the invested currency exceeds the cost of borrowing the funding currency, resulting in a net profit.
- Risk Assessment: Carry traders must consider the stability and economic fundamentals of the countries involved, as well as the potential for interest rate changes or market volatility.
Implementation:
Scalping Trade Strategy
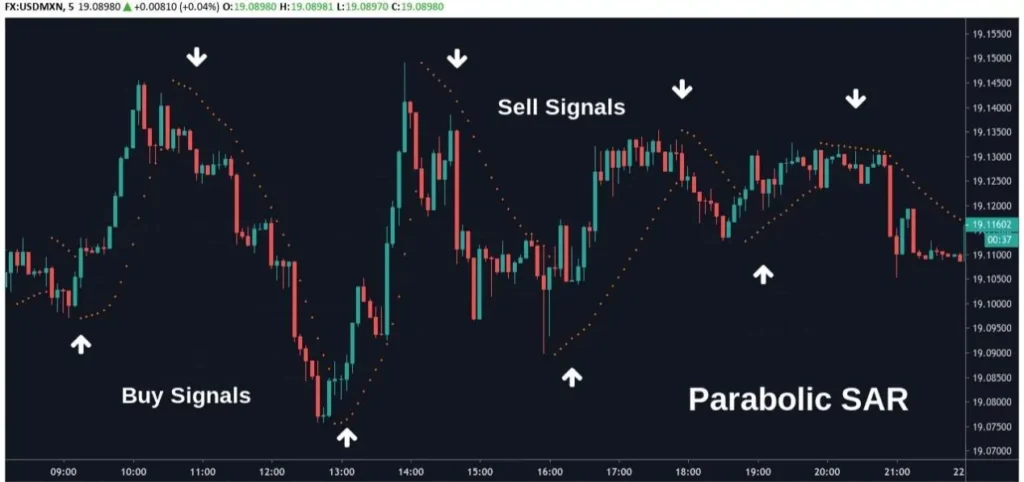
Scalping is an intense, fast-paced Forex Trading Strategies that aims to profit from small price movements, often holding positions for just a few minutes or even seconds. Scalpers seek to capitalize on the constant fluctuations in currency prices, making numerous trades throughout the day to accumulate small gains that add up to significant profits over time.
Key Principles
- High-Frequency Trading: Scalpers execute a large number of trades, sometimes hundreds per day, focusing on quick entry and exit points.
- Small Price Movements: Profits are derived from minimal price changes, often measured in pips or fractions of pips.
- Short Holding Periods: Positions are typically held for very brief periods, ranging from a few seconds to several minutes.
- Tight Stop Losses: Scalpers use extremely tight stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on each trade.
- High Leverage: To make the small price movements meaningful, scalpers often use high leverage to increase their potential profits.
Implementation:
👉 Choosing the Right Forex Trading Strategies

When selecting a Forex Trading Strategies, consider the following key factors to ensure it aligns with your goals, resources, and market understanding:
- Trading Style
- Market Conditions
- Capital
- Experience Level
- Currency Pairs
- Technological Capabilities
📌 Advanced Forex Trading Strategies
⚙ Multi-Time Frame Analysis
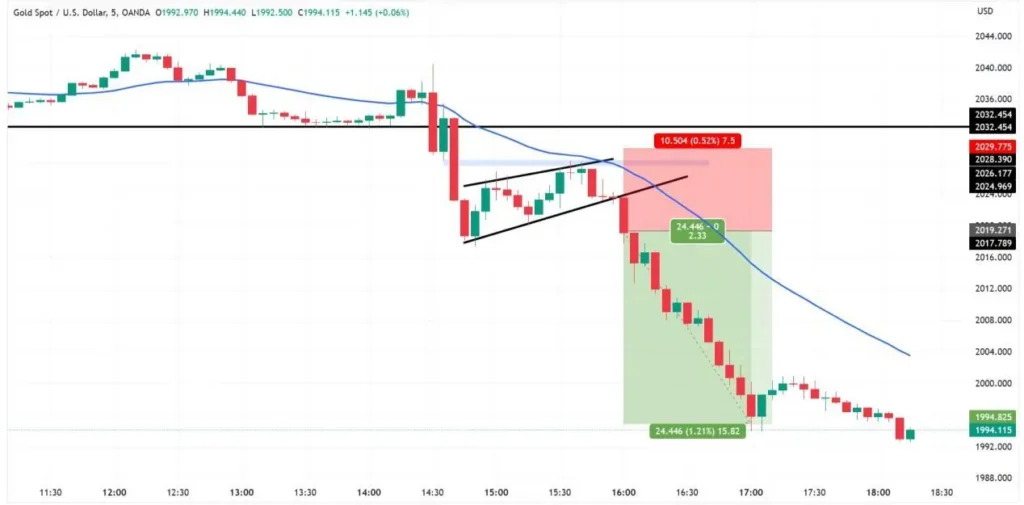
Multi-time frame analysis is a powerful strategy that involves analyzing currency pairs across different time frames to gain a more comprehensive view of market trends and identify potential entry and exit points. By examining price action on multiple time frames, traders can make more informed decisions and increase the probability of success.
Key Aspects of Multi-Timeframe Analysis Include
- Higher time frames: Traders start by analyzing higher time frames (e.g., daily or weekly charts) to identify the overall market trend and key support and resistance levels. This helps them determine the general direction of the market and potential areas of interest.
- Lower time frames: Once the overall trend is established, traders then drill down to lower time frames (e.g., hourly or 15-minute charts) to pinpoint specific entry and exit points. Lower time frames provide a more granular view of price action and can help traders identify optimal trade setups.
- Confluence: Multi-time frame analysis seeks to find confluence between different time frames. When the trend and key levels align across multiple time frames, it increases the likelihood of a successful trade.
- Risk management: By considering multiple time frames, traders can better manage their risk by placing stop-losses and take-profit levels at key support and resistance areas identified on higher time frames.
⚙ Harmonic Pattern Trading
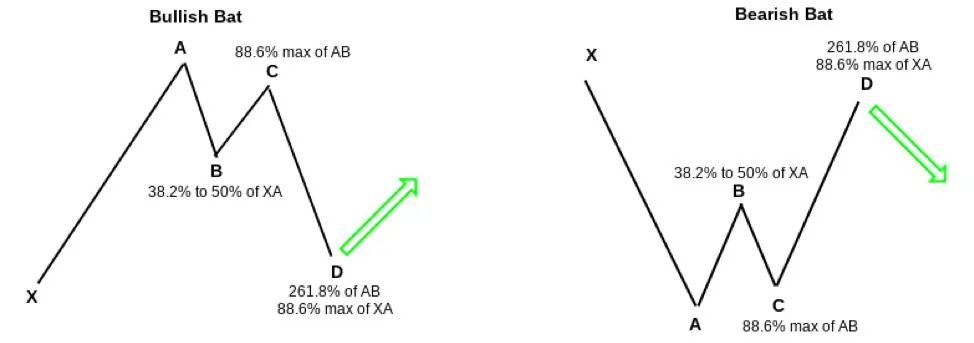
Harmonic pattern trading is an advanced strategy that uses Fibonacci ratios to identify potential reversal points in the market based on specific geometric price patterns. These patterns, such as the Gartley, Butterfly, Bat, and Crab, are formed by price movements that adhere to specific Fibonacci ratios.
Key Elements of Harmonic Pattern Trading Include
- Pattern recognition: Traders must learn to identify the various harmonic patterns and their specific Fibonacci ratios. This requires a keen eye for price action and an understanding of how these patterns form.
- Fibonacci ratios: Harmonic patterns rely heavily on Fibonacci ratios, such as 0.382, 0.618, 1.272, and 1.618. These ratios are used to determine the key price levels within the pattern and potential reversal zones.
- Confirmation: Once a harmonic pattern is identified, traders should wait for confirmation before entering a trade. This can include price action confirmation, such as a bullish or bearish candlestick pattern, or additional technical indicators like RSI or MACD.
- Risk management: As with any trading strategy, proper risk management is crucial. Traders should determine their stop-loss and take-profit levels based on the specific harmonic pattern and the market context.
⚙ Grid Trading
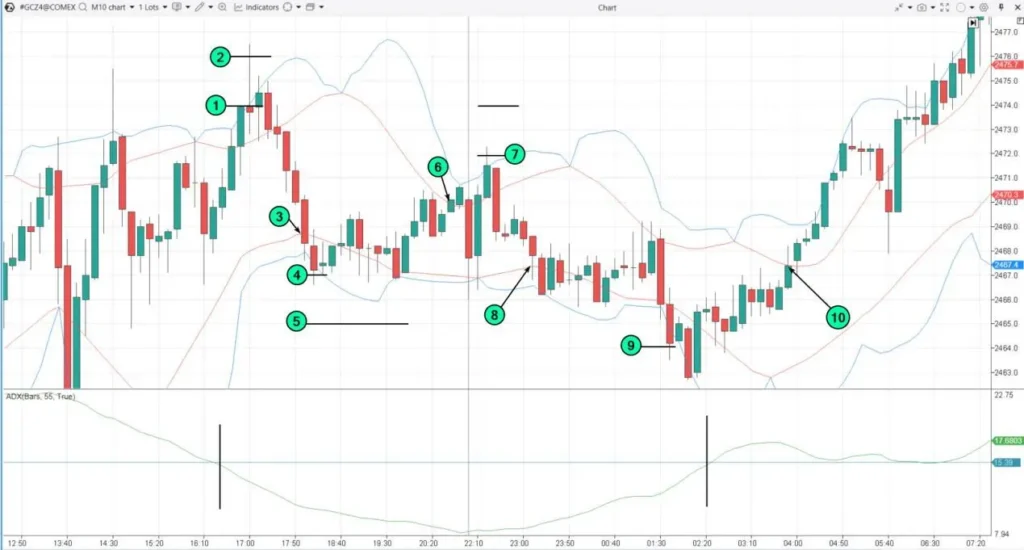
Grid trading is a mechanical trading strategy that involves placing multiple buy and sell orders at predetermined price intervals above and below the current market price. The goal is to profit from price oscillations within a defined range.
Key Aspects of Grid Trading Include
- Grid setup: Traders determine the size of the grid by setting a specific price interval between each buy and sell order. This interval can be based on factors such as the average true range (ATR) or a percentage of the current price.
- Order placement: Buy orders are placed at regular intervals below the current market price, while sell orders are placed at regular intervals above the current price. As the price fluctuates, these orders are executed, and new orders are placed to maintain the grid.
- Profit potential: The profit potential of grid trading comes from the accumulation of small gains from each buy and sell order. As the price oscillates within the grid, the trader aims to profit from the difference between the buy and sell orders.
- Risk management: Grid trading requires careful risk management, as a strong trend can lead to multiple consecutive losing trades. Traders should determine the appropriate grid size and order intervals based on their risk tolerance and market volatility.
⚙ News Trading
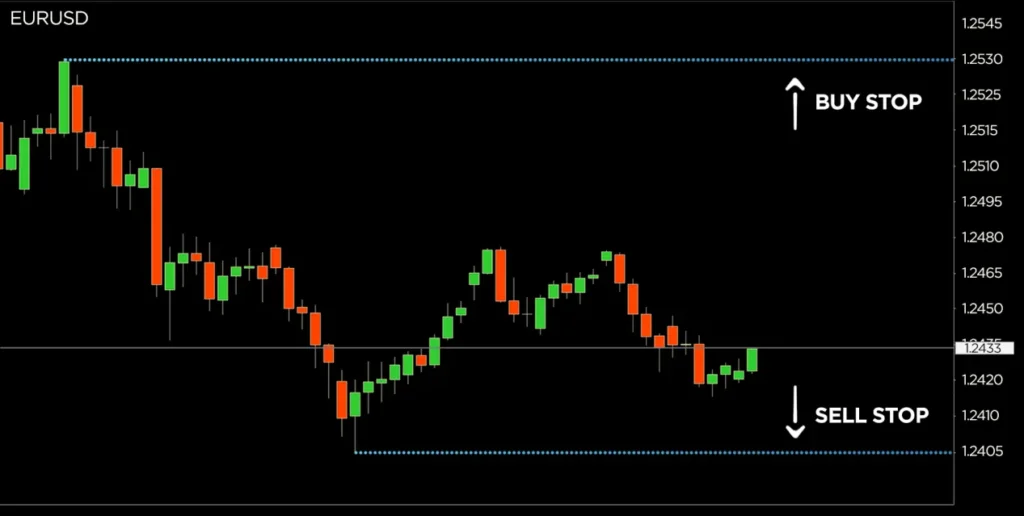
News trading is a strategy that capitalizes on the volatility surrounding major economic announcements and events. This strategy requires quick decision-making and a solid understanding of fundamental analysis.
Key Elements of News Trading Include
- Economic calendar: Traders must stay informed about upcoming economic releases and events that can impact currency pairs. This includes central bank meetings, GDP reports, inflation data, and employment figures.
- Fundamental analysis: A solid understanding of fundamental analysis is crucial for news trading. Traders must be able to interpret economic data and assess its potential impact on currency pairs.
- Volatility: Economic news releases often lead to increased market volatility, presenting both opportunities and risks for traders. Traders must be prepared for rapid price movements and have a clear plan for managing their positions.
- Quick decision-making: News trading requires the ability to make quick decisions based on the actual data release and market reaction. Traders must be able to interpret the news and execute trades promptly to capitalize on the resulting price movements.
- Risk management: Given the high volatility associated with news events, proper risk management is essential. Traders should use appropriate position sizing and have clear stop-loss and take-profit levels in place.
Questions You Might Search For
What is The Purpose of Forex Trading Strategies?
Forex trading strategies help traders identify profitable opportunities and manage risk effectively in the currency market.
How does Trend following work in Forex?
Trend following involves identifying market momentum and entering trades that align with the prevailing trend direction.
What is Range Trading in Forex?
Range trading capitalizes on price movements within defined support and resistance levels, buying at support and selling at resistance.
What is The Carry Trade Strategy?
The carry trade strategy involves borrowing a low-interest currency to invest in a high-interest currency, profiting from the differential.
How do Scalping Strategies operate in Forex?
Scalping strategies focus on making numerous quick trades to profit from small price movements, often holding positions for minutes.
What is Multi-Timeframe analysis in Forex Trading?
Multi-time frame analysis involves examining price action across different time frames to identify trends and optimize entry and exit points.
How does Harmonic Pattern Trading Work?
Harmonic pattern trading uses Fibonacci ratios to identify specific price patterns, indicating potential reversal points in the market.
What is Grid Trading in Forex?
Grid trading places multiple buy and sell orders at set intervals around the current price, aiming to profit from market fluctuations.
🔗 Conclusion

Forex trading strategies provide a structured approach to the currency markets. While no single strategy guarantees success, having a well-defined plan can significantly improve your trading performance. Remember to choose a strategy that aligns with your trading style, risk tolerance, and market analysis. Continuously evaluate and refine your approach as you gain experience in the forex market.
As you develop your Forex Trading Strategies skills, consider combining elements from different strategies to create a personalized approach that works best for you. Always prioritize risk management and stay informed about market conditions and economic factors that can impact currency movements.
By mastering Forex Trading Strategies and maintaining discipline in your trading, you'll be better equipped to capitalize on opportunities in the world's largest financial market.

![Derivatives in Forex Trading 📖 Forex Glossary [2025 Edition] 14 Derivatives](https://fxparkey.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Derivatives-2-300x189.webp)

![Equity in Forex Trading 📖 Forex Glossary [2025 Edition] 16 Equity](https://fxparkey.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Equity-300x189.webp)
![Demo Account in Forex Trading 📖 Forex Glossary [2025 Edition] 17 Demo Account](https://fxparkey.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/Demo-Account-1-300x189.webp)
![Evaluation Process in Forex Trading 📖 Forex Glossary [2025 Edition] 19 Evaluation Process](https://fxparkey.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/the-Evaluation-Process-300x189.webp)